특징
- Lipid nanoparticles (LNPs, 지질나노입자)는 비바이러스성 약물 전달 시스템으로, RNA 기반 약물 (mRNA, siRNA) 및 유전자편집도구 (CRISPR)와 같은 생리활성 분자를 in vitro 및 in vivo 내에서 표적 세포로 캡슐화하고 운반하기 위해 이용됩니다.
- LNP는 지질 기반 전달 시스템으로, 나노미터 크기의 입자(< 100nm)로 reverse micelle에 캡슐화된 cargo molecule로 채워진 내부 코어를 둘러싼 lipid monolayer shell로 구성됩니다.
- LNP는 다양한 질병과 mRNA 백신 개발에서 잠재력이 입증되었습니다.
- LNP의 구성요소인 Ionizable lipids, PEG-lipids, Phospholipids, Sterol lipid 및 Liposome/lipoplex transfection enhancer를 제공합니다.
주요 LNP components
| Cat. No. |
Product |
Activity |
| 8902 |
Angiopep-2-Cys |
Binds
to LRP1 and facilitates receptor-mediated transcytosis of cargo across the
BBB |
| 7945 |
Cholesterol |
Component of lipid nanoparticles (LNPs);
modulator of lipid bilayer fluidity |
| 8904 |
Cys-T7 Peptide |
Targeting peptide for the transferrin
receptor (N-term Cys) |
| 7176 |
DC-Cholesterol hydrochloride |
Cationic cholesterol derivative |
| 8895 |
DLin-KC2-DMA |
Ionizable cationic lipid |
| 7946 |
DLin-MC3-DMA |
Component of lipid nanoparticles (LNPs);
ionizable cationic lipid |
| 7944 |
DMG-PEG 2000 |
PEGylated myristoyl diglyceride; commonly
used in the formation of lipid nanoparticles (LNPs) |
| 7175 |
DOPE |
Liposome/lipoplex transfection enhancer |
| 7179 |
DOTAP |
Cationic agent for liposome and LNP
formation |
| 7943 |
DSPC |
Neutral phospholipid; component of lipid
nanoparticles (LNPs) |
| 8837 |
DSPE-PEG 2000 Azide |
PEGylated DSPE with azide reactive group |
| 8838 |
DSPE-PEG 2000 Biotin |
Biotinylated DSPE PEG lipid |
| 7947 |
DSPE-PEG 2000 Maleimide |
PEGylated DSPE with a maleimide reactive
group |
| 8889 |
MC3 LNP Luciferase |
Dlin-MC3 containing LNP for in vitro and in vivo delivery of luciferase mRNA |
| 8903 |
RVG29-Cys |
Nicotinic acetylcholine receptor
targeting peptide for neuronal delivery |
| 8909 |
SM 102 |
Cationic ionizable lipid |
Lipid Nanoparticles (LNP)의 구조
LNP는 Ionizable lipids(DLin-MC3-DMA, #7946), PEG-lipids(DSPC, #7943), Phospholipids(DMG-PEG 2000, #7944), Sterol lipids(Cholesterol, #7945) 네 종류의 주요 요소로 형성됩니다. Liposome과 같은 다른 nanocarrier와 비해, LNP는 더 안정적이고, 융합성이 낮으며, 배치간 변동이 적도록 제작됩니다. LNP는 또한 세포독성과 면역원성이 낮고, transfection 효율과 핵산 encapsulation 효율이 높습니다.
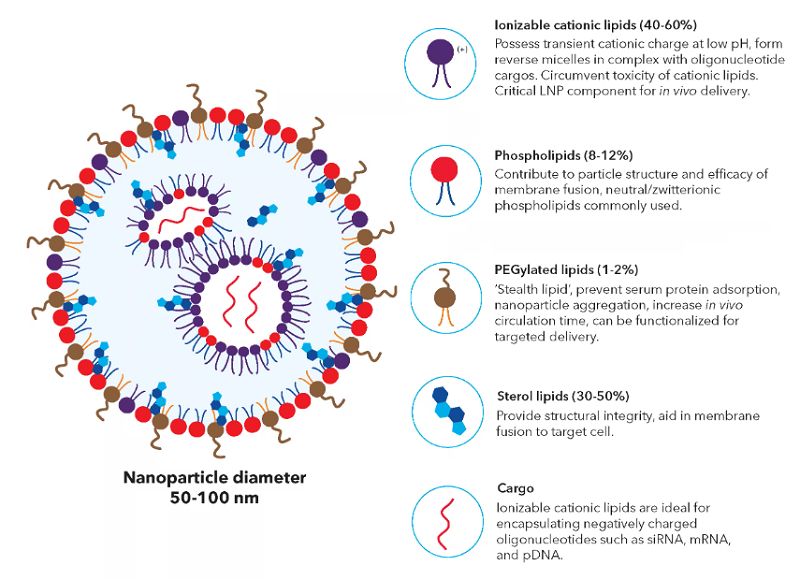
그림 1. Structure and component of lipid nanoparticle carriers. Nucleic acid cargos are stabilized by the ionizable lipids and contained in reverse lipid micelles inside the nanoparticle. The outer membrane with PEGylated lipids provides protection for the core.
Lipid Nanoparticles (LNP)의 적용
유전 의학은 백신, 암 면역 요법 개발, 희귀 유전 및 undruggable disease의 치료를 포함하는 광범위한 분야에 적용할 수 있습니다. 짧은 mRNA, 작은 siRNA, FDA의 승인을 받은 유전자 편집 구조물과 같은 핵산 기반 약물의 수가 증가하고 있습니다. 그러나 핵산 기반 약물 개발에는 주요 장애물이 있습니다. 핵산 기반 약물은 크기가 크고 극성이 있으며 대사적으로 불안정합니다. 변형되지 않은 올리고뉴클레오티드의 세포 흡수 속도는 매우 낮습니다. 또한, RNA는 일반적으로 세포 내 반감기가 짧고 biological fluids에서 흔히 발견되는 exonucleases 및 endonucleases에 의해 쉽게 분해됩니다. 따라서 신뢰할 수 있는 전달 시스템은 모든 유전 의약품이 표적 부위에 도달하는 데 필수적입니다.
LNP 시스템은 일반적으로 임상적으로 진보된 비바이러스성 유전자 전달 시스템에 사용됩니다. LNP는 바이러스 전달 시스템에 비해 합성하기가 상대적으로 쉽고 제조 비용이 저렴하며 일관된 효율성으로 확장하기 쉽습니다. 또한, 유전자 전달을 위한 LNP의 사용은 in vivo 유전자 치료의 안전성 프로필을 개선했습니다 .
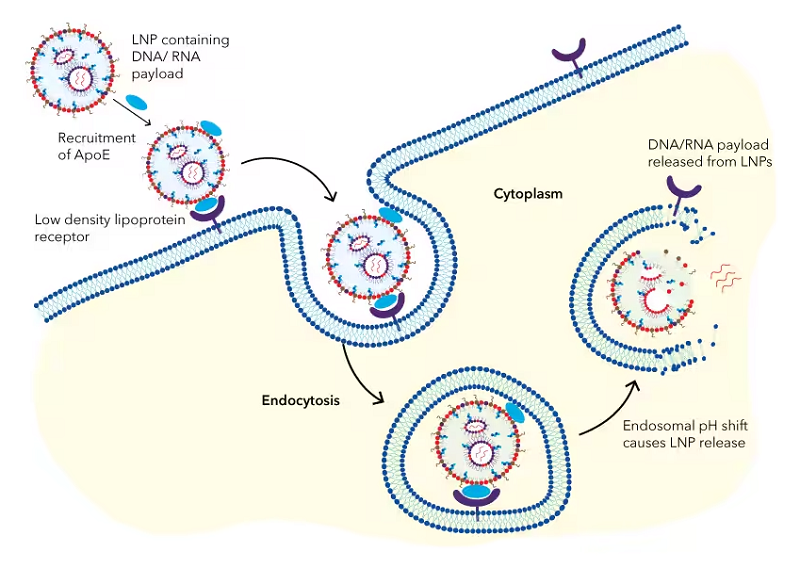
그림 2. In vivo delivery of oligonucleotides to hepatocytes using LNPs. Endogenous ApoE in the blood compartment is recruited to the LNP surface after IV administration. The ApoE-LNPs are recognized by ApoE-binding receptors on hepatocytes resulting in uptake of the LNPs into the cell by endocytosis. The ionizable lipids are protonated at low pH in the endosome, which leads to the destabilization of the endosomal membrane and the release of the payload into the cytoplasm.
Lipid Nanoparticles (LNP)의 연구
Future Direction of LNP Research: Tissue-Specific Delivery
세포 표적화를 가능하게 하는 전달 시스템은 나노의학 분야의 연구 초점입니다. 예를 들어, 암 면역요법에서 키메라 항원 수용체(CAR) T 세포 요법은 전이성 암 및 혈액암 치료에 유망한 것으로 나타났습니다. 이러한 T 세포는 유전자 변형 T 세포 수용체(TCR)를 발현하도록 유전적으로 변형되어 암세포를 특이적으로 표적화하고 제거합니다. 그러나 CAR-T 세포는 일반적으로 생체 외에서 생성되므로 비용이 많이 들 수 있습니다. 또한, T 세포는 외인성 mRNA에 의한 형질감염에 대한 저항성이 악명 높습니다. Tombáczet al. CD4 표적화 LNP는 일반적인 절차에 두 가지 추가 단계를 추가하여 합성할 수 있음을 입증했습니다. 즉, mRNA payload가 LNP에 캡슐화된 후 DSPE-PEG 2000 Maleimide(Cat. No. 7947)가 포스트-외막에 통합됩니다. 삽입 기술. CD4에 특이적인 항체(Abs)는 SATA (N-succinimidyl S-acetylthioacetate)-maleimide 접합 화학을 통해 LNP에 접합될 수 있습니다. 마우스에 Abs-LNPs-mRNA 구축물을 전신 주사한 후, 리포터 유전자 발현은 비장 및 림프절에서 CD4+ T 세포의 약 60% 및 40%에서 각각 나타납니다. 이 LNP 기반 T 세포 표적화 mRNA 전달 시스템은 생체 내 T 세포 조작을 위한 강력하고 신속한 방법을 제공합니다.
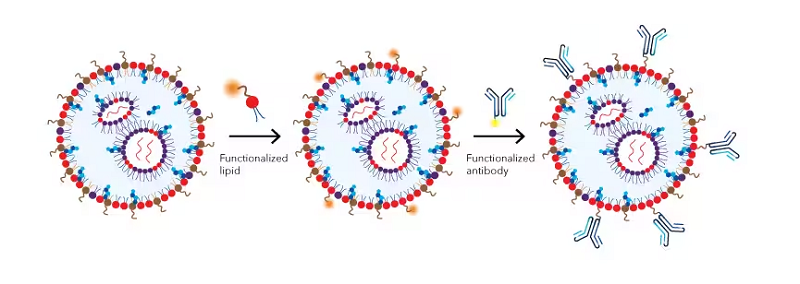
그림 3. Incorporating a targeting moiety onto the LNP surface. A two step reaction is used to preserve the functions of the targeting moiety. In the first step, functionalized lipids form micelles that preferentially insert into the outer membrane of the LNP and introduce the reactive chemical groups (e.g. maleimide) to LNP surface. In the second step, the targeting moiety, such as an antibody, is conjugated to the surface of the LNP via the reactive groups.